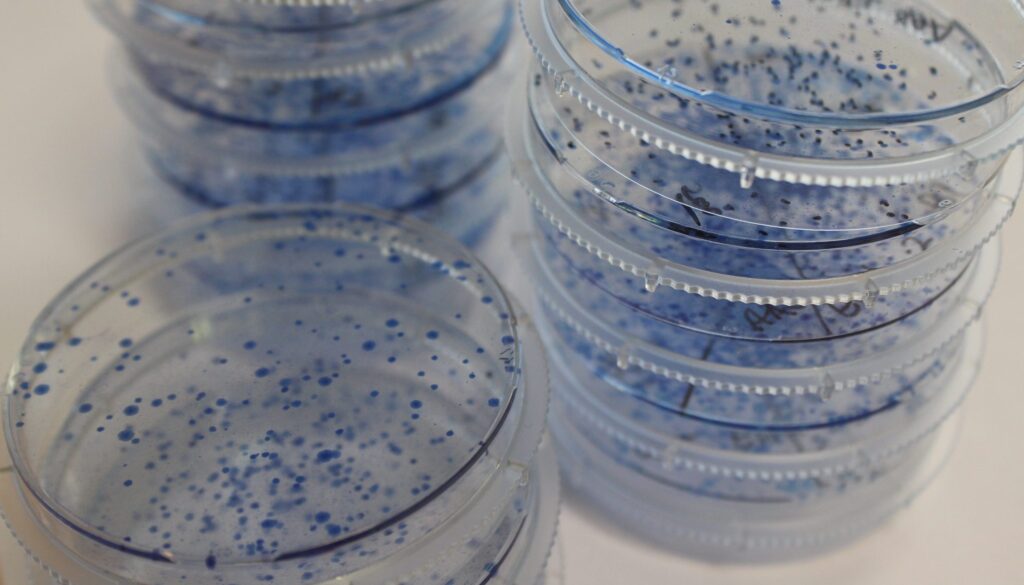
The clonogenic assay, also known as the colony formation assay, is an in vitro technique widely used in cancer research and radiation biology to assess the reproductive potential of cells after treatment with various agents (e.g., drugs, radiation) or genetic modifications. It measures the ability of a single cell to grow and form a colony consisting of at least 50 cells over a defined period. This assay provides crucial information about the long-term survival and proliferative capacity of cells, reflecting their clonogenic survival.
Test Details
Procedure
- A carefully counted number of individual cells was placed into sterile dishes containing growth medium. These cells were then allowed some time to attach themselves to the surface of the dishes.
- The cells were either left alone or were exposed to a specific treatment, like a drug or radiation. Afterward, they were provided with fresh growth medium and left to incubate in controlled conditions for a few weeks so that any surviving cells could multiply.
- The growth medium was removed, and the cells were fixed to preserve them. Then, a staining solution was applied to make the groups of cells (colonies) visible. Finally, the number of colonies containing a certain number of cells was counted under a microscope or by eye.
Contact Us
Have questions about this test? Send us a message and we'll get back to you as soon as possible.

